Extracellular Matrix Proteinases
Michel Goldberg1*
1Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Fundamental and Biomedical Sciences, INSERM UMR-S 1124 Paris Cite University, France
*Corresponding Author: Michel Goldberg, Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Fundamental and Biomedical Sciences, INSERM UMR-S 1124 Paris Cite University, France; Email: [email protected]
Published Date: 18-01-2022
Copyright© 2022 by Goldberg M. All rights reserved. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
| Received 11 Nov, 2021 | Accepted 10 Jan, 2022 | Published 18 Jan, 2022 |
Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinases, known also as matrixins, cleave components of the extracellular matrix. They remodel collagen, elastin, gelatin and casein, and contribute to the MMP degradation. MMPs are secreted in latent forms (pro-MMP) and activated as zinc-dependent proteolytic enzymes in the extracellular compartment. MMPs are divided into 6 subgroups:
- Collagenases that degrade triple-helical fibrillary collagens into ¾ – ¼ fragments
- Gelatinases (A and B)
- Stromelysins
- Proteoglycanases
- Matrilysins
- Membrane-type MMPS, metalloelastase, enamelysin and others MMPs.
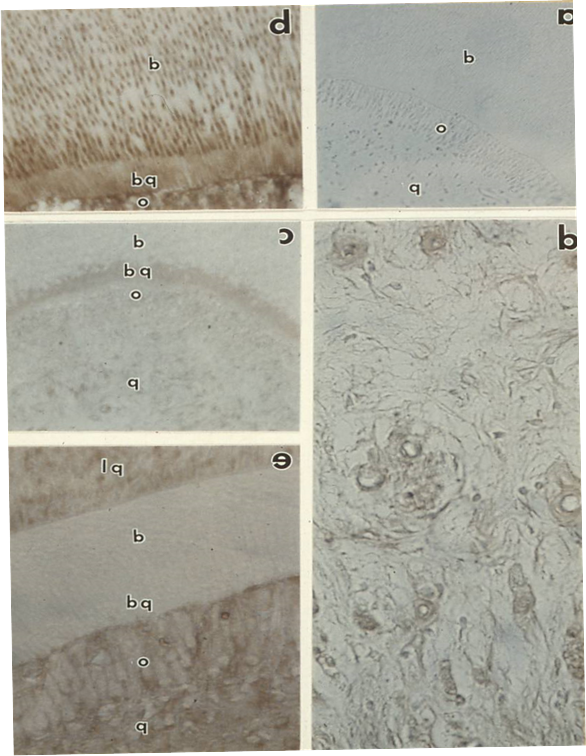
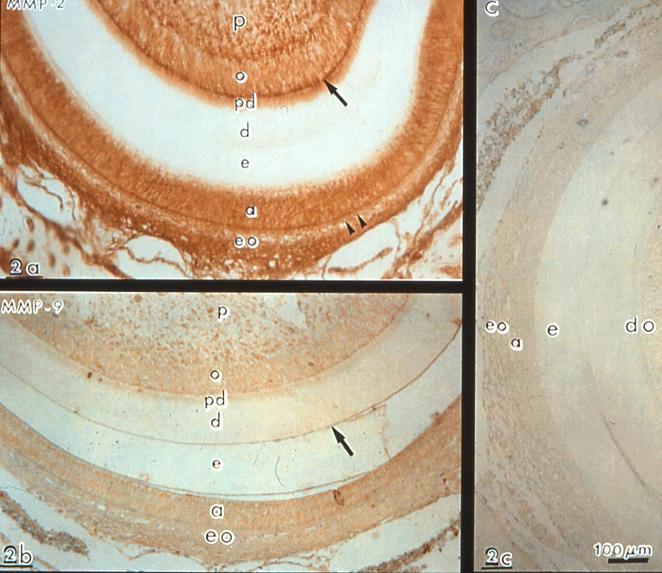
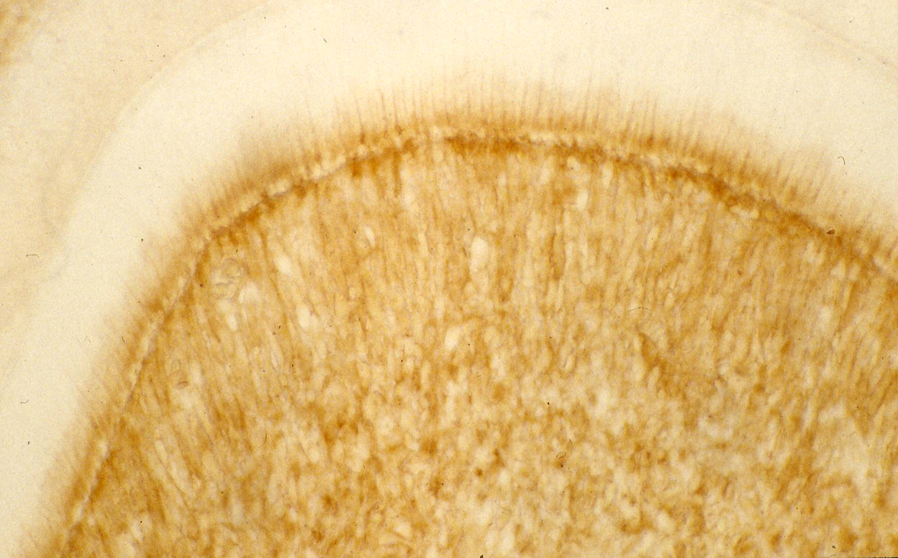
Four tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 to -4) have been identified. Enamel matrix of developing teeth MMP20 and KLK-4 were detected during the secretory stage of enamel. MMP20 null mice play role during enamel secretion, whereas KLK4 is crucial during the maturation stage. The additional roles of MMP are wound healing, cancer progression, and skeletal dysplasias. In addition, MMP inhibitors are useful in the prevention of caries progression.
Keywords
Matrix MetalloProteinases; Collagenases; Gelatinases; Stromelysin; Proteoglycanases; Matrilysins; Membrane-Type Mmps; Tissue-Inhibitors of Matrix Metalloproteinases (TIMP); Metalloelastase; Enamelysin (Mmp-20); KLK-4 (Enamel Maturation); Dental Caries