Re-Formation: Reactionary or Reparative Dentin
Michel Goldberg1*
1Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Fundamental and Biomedical Sciences, INSERM UMR-S 1124 Paris Cite University, France
*Corresponding Author: Michel Goldberg, Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Fundamental and Biomedical Sciences, INSERM UMR-S 1124 Paris Cite University, France; Email: mgoldod@gmail.com
Published Date: 20-01-2022
Copyright© 2022 by Goldberg M. All rights reserved. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
| Received 13 Dec, 2021 | Accepted 12 Jan, 2022 | Published 20 Jan, 2022 |
Abstract
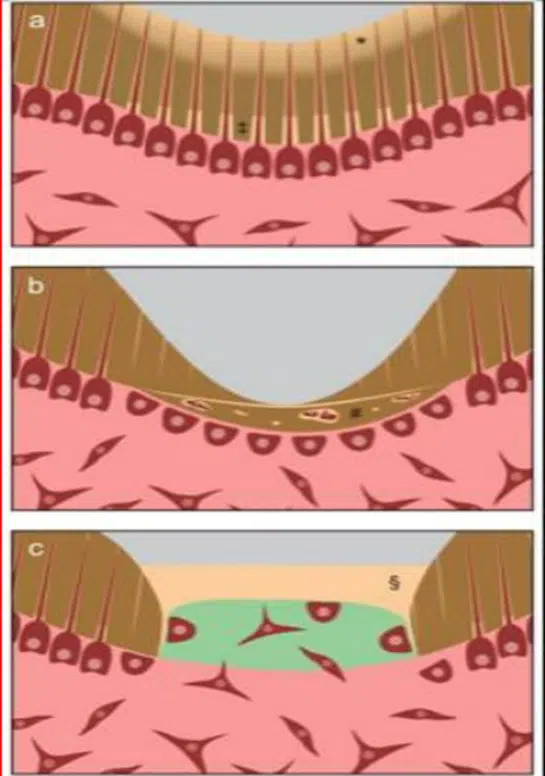
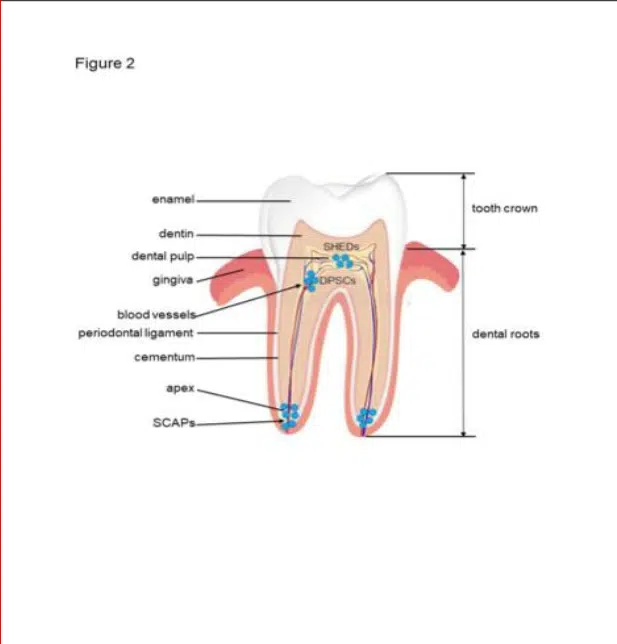
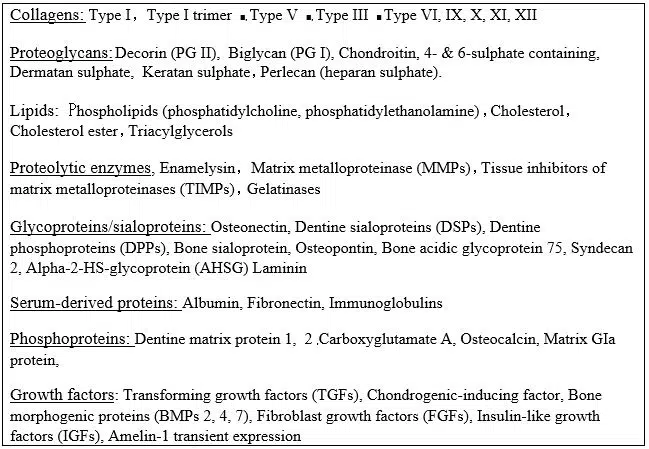
Dentin (s) are complex structures including in the crown, the formation of the mantle dentin mostly atubular, and circumpulpal dentin, crossed along its entire length by 180,000-240,000 tubules per mm2. In the root, two superficial layers (the Tomes’ granular and the hyaline Hopewell-Smith layers) limit the dentin just beneath the acellular and cellular cementum. Circumpulpal dentin is formed by intertubular and peritubular dentine. The lumens of the tubules are apparently empty or they contain unmineralized collagen fibers and/or odontoblast processes. Circumpulpal dentin includes the primary and secondary dentin, both physiological. Apexogenesis and apexification constitute two crucial events contributing to root formation, and to apical closure. The tertiary dentin is formed in reaction to caries, or wear. Intraluminal mineralization, reactionary and reparative dentins constitute a response to noxious events. Non-collagenous molecules contribute to dentin mineralization or are acting as mineralization inhibitors. Osteopontin is essential for the formation of tertiary dentin after a trauma, whereas tunnels and osteodentin labeling persisted during the formation or re-formation of a dentinal bridge.
Keywords
Dentinogenesis; Mantle Dentin; Circumpulpal Dentin; Intertubular Dentin; Peritubular Dentin; Odontoblasts; Tomes’ Granular Layer; Hyaline Hopewell-Smith Layer; Reactionary Dentin; Reparative Dentin; Tertiary Dentin; Osteopontin; Apexogenesis; Apexification